Jsoup实战——抓取正方教务系统
爬虫的原理很简单,无非就是分析HTTP(s)请求,然后通过代码模拟浏览器去发起请求,对于发起网络请求框架可选Apache的HttpClient,然后拿到网页后就需要解析网页关键内容,此时Jsoup就发挥作用了,通过节点选择器 + 表达式可以很方便的拿到想要的数据了。
HttpClient
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.httpcomponents</groupId>
<artifactId>httpclient</artifactId>
<version>4.5.2</version>
</dependency>
Jsoup
我们抓取到页面之后,还需要对页而进行解析。可以使用字符串处理工具解析页面,也可以使用正则表达式,但是这些方法都会带来很大的开发成本,所以我们需要使用一款专门解析HTML页面的技术。
jsoup介绍
Jsoup是一款Java的HTML解析器,可直接解析某个URL地址、HTML文木内容。它提供了一套非常省力的API,可通过DOM,CSS以及类似于jQuery的操作方法来取出和操作数据。
Jsoup的主要功能
1.从一个URL,文件或字符串中解析HTML;
2.使用DOM或CSS选择器来查找、取出数据;
3.可操作HTML元素、属性、文本;
Jsoup实战
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.httpcomponents</groupId>
<artifactId>httpclient</artifactId>
<version>4.5.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-log4j12</artifactId>
<version>1.7.25</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.jsoup</groupId>
<artifactId>jsoup</artifactId>
<version>1.11.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-io</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-io</artifactId>
<version>2.6</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-lang3</artifactId>
<version>3.7</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
@Test
public void testUrl() throws Exception {
Document document = Jsoup.parse(new URL("http://zouchanglin.cn"), 5000);
String title = document.getElementsByTag("title").first().text();
System.out.println(title);
}
@Test
public void testString() throws Exception {
String html = FileUtils.readFileToString(new File("C:\\Users\\15291\\Desktop\\d4c0f50720a538647399fc1363896cce.html"), "UTF-8");
Document document = Jsoup.parse(html);
String title = document.getElementsByTag("title").first().text();
System.out.println(title);
}
@Test
public void testFile() throws Exception {
Document document = Jsoup.parse(new File("C:\\Users\\15291\\Desktop\\d4c0f50720a538647399fc1363896cce.html"), "UTF-8");
String title = document.getElementsByTag("title").first().text();
System.out.println(title);
}
虽然使用Jsoup可以替代HttpClient直接发起请求解析数据,但是往往不会这样用,因为实际的开发过程中,需要使用到多线程,连接池,代理等等方式,而Jsoup对这些的支持并不是很好,所以我们一般把Jsoup仅仅作为Html 解析工具使用。
Dom方式遍历文档
元素获取 1、根据id查询元素getElementByld 2、根据标签获取元素getElementsByTag 3、根据class获取元素getElementsByClass 4、根据属性获取元素getElementsByAttribute
元素中获取数据 1、从元素中获取id 2、从元素中获取className 3、从元素中获取属性的值 attr 4、从元素中获取所有属性attributes 5、从元素中获取文本内容text
Selector选择器
tagname:通过标签查找元素,比如: span
#id:通过ID查找元素,比如: #city_bj
.class:通过class名称查找元素,比如: .class_a
[attribute]:利用属性查找元素,比如:[abc]
[attr=value]:利用属性值来查找元素,比如: [class=s_name]
Selector选择器组合使用
el#id:元素+ID,比如:h3#3city_bj
el.class:元素+class,比如:li.class_a
el[attr]:元素+属性名,比如:span[abc]
任意组合:比如: span[abc].s_name
ancestor child:查找某个元素下子元素,比如: .city_con li查找city_con下的所有li
parent > child:查找某个父元素下的直接子元素,比如:.city_con > ul > li查找city_con第一级(直接子元素)的ul,再找所有ul下的第一级li
parent > *:查找某个父元素下所有直接子元素
package jsoup;
import org.apache.commons.io.FileUtils;
import org.jsoup.Jsoup;
import org.jsoup.nodes.Attributes;
import org.jsoup.nodes.Document;
import org.jsoup.nodes.Element;
import org.jsoup.select.Elements;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
public class JsoupFirstTest {
@Test
public void testUrl() throws Exception {
Document document = Jsoup.parse(new URL("http://zouchanglin.cn"), 5000);
String title = document.getElementsByTag("title").first().text();
System.out.println(title);
}
@Test
public void testString() throws Exception {
String html = FileUtils.readFileToString(new File("C:\\Users\\15291\\Desktop\\d4c0f50720a538647399fc1363896cce.html"), "UTF-8");
Document document = Jsoup.parse(html);
String title = document.getElementsByTag("title").first().text();
System.out.println(title);
}
@Test
public void testFile() throws Exception {
Document document = Jsoup.parse(new File("C:\\Users\\15291\\Desktop\\d4c0f50720a538647399fc1363896cce.html"), "UTF-8");
String title = document.getElementsByTag("title").first().text();
System.out.println(title);
}
@Test
public void testDom() throws Exception {
/**
* 1、根据id查询元素getElementByld
* 2、根据标签获取元素getElementsByTag
* 3、根据class获取元素getElementsByClass
* 4、根据属性获取元素getElementsByAttribute
*/
Document document = Jsoup.parse(new File("C:\\Users\\15291\\Desktop\\d4c0f50720a538647399fc1363896cce.html"), "UTF-8");
Element element = document.getElementById("threeSpan");
System.out.println("threeSpan内容是:" + element);
System.out.println(element.getElementsByTag("a").first().attr("href"));
Elements spans = document.getElementsByTag("span");
for(Element el: spans) System.out.println(el);
System.out.println(document.getElementsByAttributeValue("type", "button").first());
System.out.println(document.getElementsByAttributeValue("type", "button").first().attr("value"));
/**
* 1、从元素中获取id
* 2、从元素中获取className
* 3、从元素中获取属性的值 attr
* 4、从元素中获取所有属性attributes
* 5、从元素中获取文本内容text
*/
Element button = document.getElementsByAttributeValue("type", "button").first();
Attributes attributes = button.attributes();
System.out.println(attributes);
}
@Test
public void testSelector() throws Exception {
/**
* `tagname`:通过标签查找元素,比如: `span`
* `#id`:通过ID查找元素,比如: `#city_bj`
* `.class`:通过class名称查找元素,比如: `.class_a`
* `[attribute]`:利用属性查找元素,比如:`[abc]`
* `[attr=value]`:利用属性值来查找元素,比如: `[class=s_name]`
*/
Document document = Jsoup.parse(new File("C:\\Users\\15291\\Desktop\\d4c0f50720a538647399fc1363896cce.html"), "UTF-8");
Elements span = document.select("span");
System.out.println(span);
System.out.println("===============================");
System.out.println(document.select("#threeSpan").first());
System.out.println(document.select("#threeSpan").first().text());
}
@Test
public void testSelectorTwo() throws Exception {
/**
* `el#id`:元素+ID,比如:`h3#3city_bj`
* `el.class`:元素+class,比如:`li.class_a`
* `el[attr]`:元素+属性名,比如:`span[abc]`
* 任意组合:比如: `span[abc].s_name`
* `ancestor child`:查找某个元素下子元素,比如: `.city_con li`查找""city_con"下的所有li
* `parent > child`:查找某个父元素下的直接子元素,比如:`.city_con > ul > li`查找city_con第一级(直接子元素)的ul,再找所有ul下的第一级li
* `parent > *`:查找某个父元素下所有直接子元素
*/
Document document = Jsoup.parse(new File("C:\\Users\\15291\\Desktop\\d4c0f50720a538647399fc1363896cce.html"), "UTF-8");
System.out.println(document.select("span#oneSpan").first());
System.out.println(document.select("span[style]").first());
System.out.println(document.select(".my_div div"));
System.out.println("======================================");
System.out.println(document.select(".my_div > div"));
System.out.println("======================================");
System.out.println(document.select(".my_div *"));
}
@Test
public void course() throws IOException {
Document document = Jsoup.parse(new File("C:\\Users\\15291\\Desktop\\new 10.html"), "UTF-8");
Element tbody = document.select("table.blacktab > tbody").first();
Elements tds = tbody.select("tr td");
for(Element td: tds){
String tdContent = td.text();
if(tdContent.contains("{")){
System.out.println(tdContent);
handel(tdContent);
}
}
}
private void handel(String tdContent) {
String[] split = tdContent.split(" ");
System.out.print(split[0] + "\t");
System.out.print(split[1].substring(0, 2) + "\t");
System.out.print(split[1].substring(split[1].indexOf("第")+1, split[1].indexOf("节")) + "\t");
System.out.print(split[1].substring(split[1].indexOf("{")+2, split[1].indexOf("}") - 1) + "\t");
System.out.print(split[2] + "\t");
System.out.print(split[3] + "\t");
System.out.println("");
}
}
正方教务爬虫
1、引入依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.gitee.zouchanglin</groupId>
<artifactId>spider_xpu</artifactId>
<version>1.2</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>jitpack.io</id>
<url>https://jitpack.io</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
2、使用示例
import cn.zouchanglin.spider_xpu.SpiderResult;
import cn.zouchanglin.spider_xpu.cache.ResultCache;
import cn.zouchanglin.spider_xpu.core.SpiderCore;
import javax.security.auth.login.LoginException;
import java.awt.*;
import java.net.URI;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// Key就是一个标识用户唯一的键(如可以传OpenId、UnionId、学号、身份证号等)
// TODO 填充Key、userId、password等字段
String key = "";
String userId = "";
String passsword = "";
// 1、获取验证码URL
String url = SpiderCore.getCheckCodeUrl(key);
// 打开浏览器并输入验证码
Desktop desktop = Desktop.getDesktop();
if (Desktop.isDesktopSupported() && desktop.isSupported(Desktop.Action.BROWSE)) {
URI uri = new URI(url);
desktop.browse(uri);
}
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String code = scanner.nextLine();
// 记录用时
long millis = System.currentTimeMillis();
SpiderResult spiderResult = null;
try {
// 2、获取同步调用结果只返回用户信息 + 当前学年的课表
spiderResult = SpiderCore.go(userId, password, code, key);
}catch (LoginException e){
// 登录失败
System.out.println(e.toString());
}
// 同步调用结果
System.out.println("同步调用只返回用户信息+当前学年的课表:" + spiderResult);
System.out.println("执行耗时:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - millis));
// 阻塞等待缓存池中存在结果对象
while(!ResultCache.SPIDER_RESULT_CACHE.containsKey(key));
// 取出缓存池中的结果
SpiderResult result = ResultCache.SPIDER_RESULT_CACHE.get(key);
System.out.println(result);
//TODO 持久化
System.out.println("完成持久化....");
// 从缓存池中移除结果对象
ResultCache.SPIDER_RESULT_CACHE.remove(key);
}
}
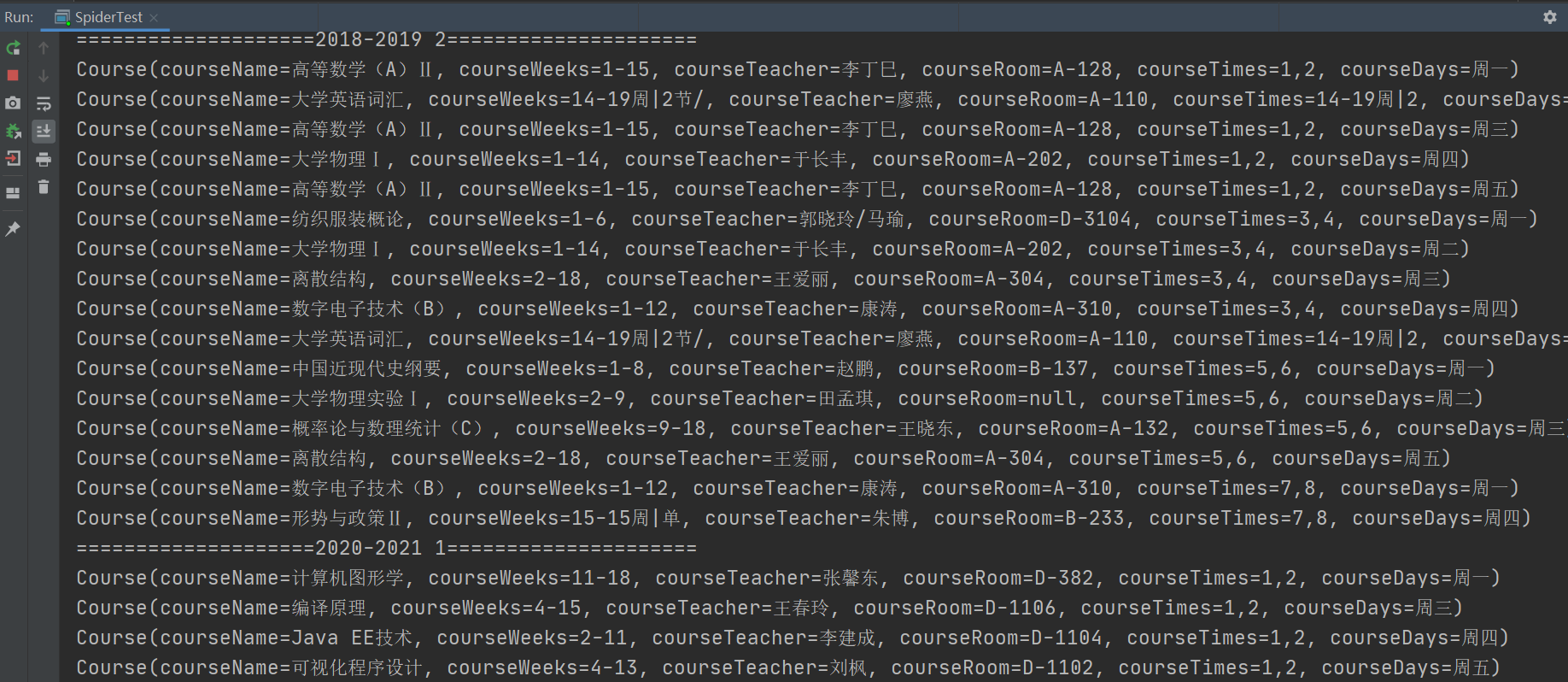
通过对学生信息和学生所有课表的爬取,效果还行: