自定义SpringBootStarter
在日常使用SpringBoot的开发中,如果想要引入某个组件,几乎都是直接引入一个SpringBootStarter就完事,分析了SpringBoot的具体启动流程以及自动配置的原理其实很容易明白官方的starter是如何运行起来的,并且我们可以制作一个自己的SpringBootStarter,并且我会把自制的SpringBootStarter推送到公服,本篇文章会记录一个完整的开发流程。
创建SpringBootStarter
其实就是创建一个普通的SpringBoot项目,无论是用Gradle还是Maven都可以,我这里选择的是Maven的方式,只不过项目的命名方式略微有所不同,因为Spring官方的starter命令为spring-boot-starter-xxx,所以我们开发的项目不要以spring-boot开头。 建议写成:xxx-spring-boot-starter,代表我们这是一个非官方的SpringBootStarter。
pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.2.6.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.github.zouchanglin</groupId>
<artifactId>example-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>example-spring-boot-starter</name>
<description>A custom Spring-Boot-Starter sample.</description>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
<spring.boot>2.2.6.RELEASE</spring.boot>
</properties>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${spring.boot}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-autoconfigure</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
我们编写一个工具类AESHandleUtil.java,假设我们需要封装一个AES加密的工具类,在这个工具类里面呢,我们想把初始化秘钥随机串的长度作为用户的自定义参数,用户可以根据自己的实际需要定义是长度为128?256还是一些其他的值。
package com.github.zouchanglin.examplespringbootstarter.util;
import javax.crypto.Cipher;
import javax.crypto.KeyGenerator;
import javax.crypto.SecretKey;
import javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.security.SecureRandom;
public class AESHandleUtil {
/**
* AES加密字符串
*
* @param content 需要被加密的字符串
* @param password 加密需要的密码
* @param length 初始化秘钥随机串的长度
* @return 密文
*/
public static byte[] encrypt(String content, String password, Integer length) {
try {
// 创建AES的Key生产者
KeyGenerator keyGenerator = KeyGenerator.getInstance("AES");
// 利用用户密码作为随机数初始化出
keyGenerator.init(length, new SecureRandom(password.getBytes()));
// 加密没关系,SecureRandom是生成安全随机数序列
// 根据用户密码,生成一个密钥
SecretKey secretKey = keyGenerator.generateKey();
// 返回基本编码格式的密钥,如果此密钥不支持编码,则返回
byte[] enCodeFormat = secretKey.getEncoded();
// 转换为AES专用密钥
SecretKeySpec key = new SecretKeySpec(enCodeFormat, "AES");
// 创建密码器
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("AES");
byte[] byteContent = content.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
// 初始化为加密模式的密码器
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, key);
// 加密
return cipher.doFinal(byteContent);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
/**
* 解密AES加密过的字符串
*
* @param content AES加密过过的内容
* @param password 加密时的密码
* @param length 初始化秘钥随机串的长度
* @return 明文
*/
public static byte[] decrypt(byte[] content, String password, Integer length) {
try {
// 创建AES的Key生产者
KeyGenerator keyGenerator = KeyGenerator.getInstance("AES");
keyGenerator.init(length, new SecureRandom(password.getBytes()));
// 根据用户密码,生成一个密钥
SecretKey secretKey = keyGenerator.generateKey();
// 返回基本编码格式的密钥
byte[] enCodeFormat = secretKey.getEncoded();
// 转换为AES专用密钥
SecretKeySpec key = new SecretKeySpec(enCodeFormat, "AES");
// 创建密码器
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("AES");
// 初始化为解密模式的密码器
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, key);
// 明文
return cipher.doFinal(content);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
}
接下来我们写一个AESHandleService.java,其实就是对工具类做了一个封装:
package com.github.zouchanglin.examplespringbootstarter.service;
import com.github.zouchanglin.examplespringbootstarter.util.AESHandleUtil;
public class AESHandleService {
private final Integer length;
public AESHandleService(Integer length) {
this.length = length;
}
public byte[] encrypt(String content, String password) {
return AESHandleUtil.encrypt(content, password, length);
}
public byte[] decrypt(byte[] content, String password) {
return AESHandleUtil.decrypt(content, password, length);
}
}
由于我们需要用户去自定义一些参数,那么我们先用一个类把自定义参数给装起来,AESHandleServiceProperties.java:如果对这些注解有疑问的话可以参考我的一篇文章《 SpringBoot自定义配置文件 》,里面对SpringBoot自定义配置的操作解释的比较详细。
package com.github.zouchanglin.examplespringbootstarter.config;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "aes")
public class AESHandleServiceProperties {
private Integer length = 128;
public Integer getLength() {
return length;
}
public void setLength(Integer length) {
this.length = length;
}
}
接下来就是最重要的一步:编写自动装配类AESHandleAutoConfiguration.java:
package com.github.zouchanglin.examplespringbootstarter.config;
import com.github.zouchanglin.examplespringbootstarter.service.AESHandleService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
@EnableConfigurationProperties(AESHandleServiceProperties.class)
public class AESHandleAutoConfiguration {
@Autowired
private AESHandleServiceProperties properties;
@Bean
AESHandleService aesHandleService() {
return new AESHandleService(properties.getLength());
}
}
当然关于Bean的实例化条件控制等,也可以加上@ConditionalOnBean与@ConditionalOnClass这些注解,在这里就不详细介绍这些注解了。官方的参数文档在这里:
《49.3.2 Bean Conditions》
。接下来需要编写spring.factories,这一步也很重要,Spring Boot自动注入的原理来源于 Spring Boot应用在启动过程中会通过SpringFactoriesLoader 加载所有 META-INF/spring.factories 文件,通过一系列的处理流程最终将spring.factories 文件中的定义的各种 beans 装载入ApplicationContext容器。所以编写spring.factories一定别忘记:
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
com.github.zouchanglin.examplespringbootstarter.config.AESHandleAutoConfiguration
最后,由于我们把测试的依赖删除了,所以测试代码也可以选择不要,那么整个工程目录如下图所示:
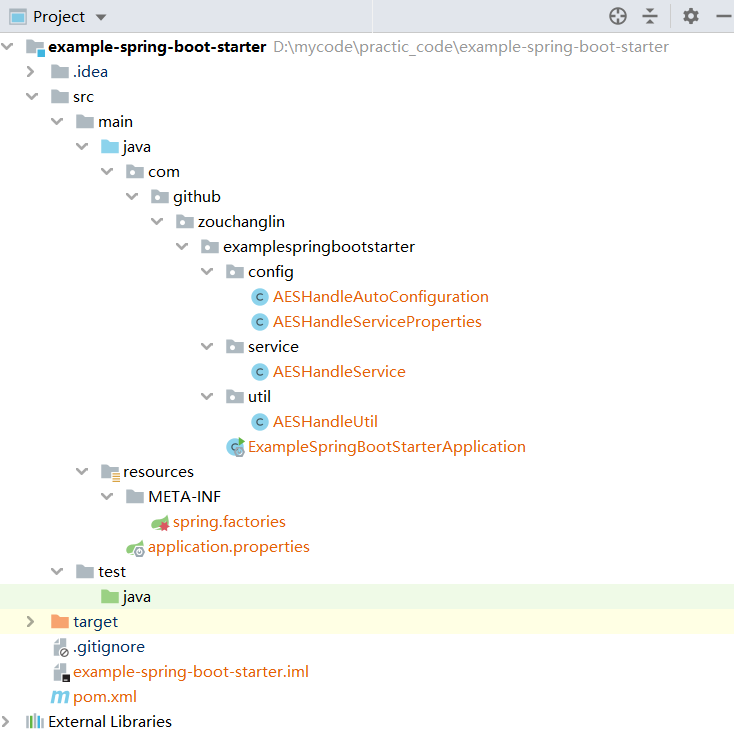
最后一步,只需要mvn install,就可以把这个starter发布到本地仓库。
测试SpringBootStarter
新建SpringBoot项目并且引入这个Starter:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.zouchanglin</groupId>
<artifactId>example-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
并且我们可以在配置文件里面指定这个starter可以配置的参数,即随机串的长度(其实不配置也有默认值)
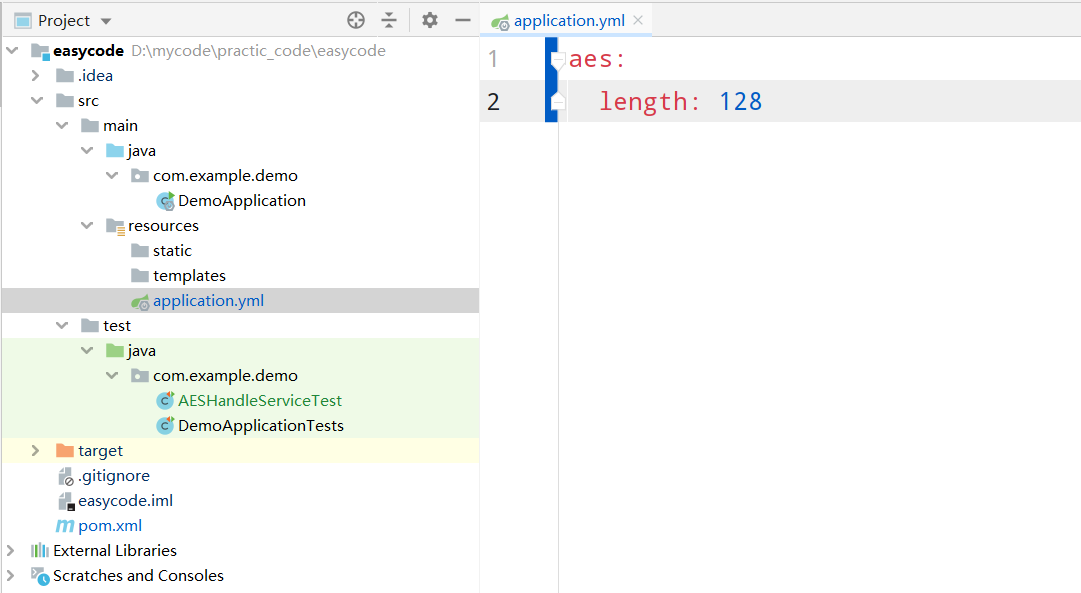
接下来通过测试代码去测试一下:
package com.example.demo;
import com.github.zouchanglin.examplespringbootstarter.service.AESHandleService;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import static org.junit.Assert.*;
@SpringBootTest
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
public class AESHandleServiceTest {
@Autowired
private AESHandleService aesHandleService;
@Test
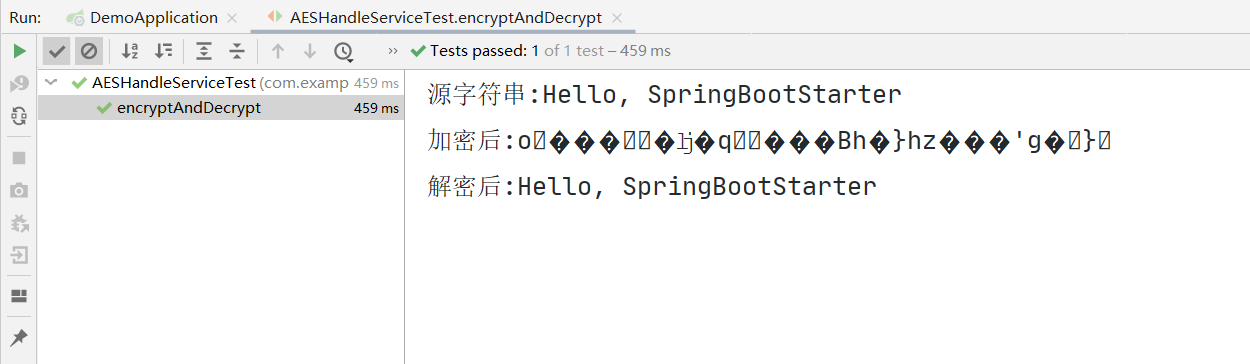
public void encryptAndDecrypt() {
String src = "Hello, SpringBootStarter";
String password = "123321";
System.out.println("源字符串:" + src);
byte[] encryptResult = aesHandleService.encrypt(src, password);
String encryptString = new String(encryptResult);
System.out.println("加密后:" + encryptString);
byte[] decryptResult = aesHandleService.decrypt(encryptResult, password);
String decryptString = new String(decryptResult);
System.out.println("解密后:" + decryptString);
assertEquals(src, decryptString);
}
}
推送至 jitpack
这个步骤比较容器,我们选择JitPack,JitPack在得到我们的GitHub账户授权之后可以拉取我们的仓库里的代码,我们只需要把项目放在GitHub上,并且打一个Tag(其实就是发布一个Release版本),我以我之前测试的MD5的一个starter来说, md5-spring-boot-starter ,只需要有发布版本即可:
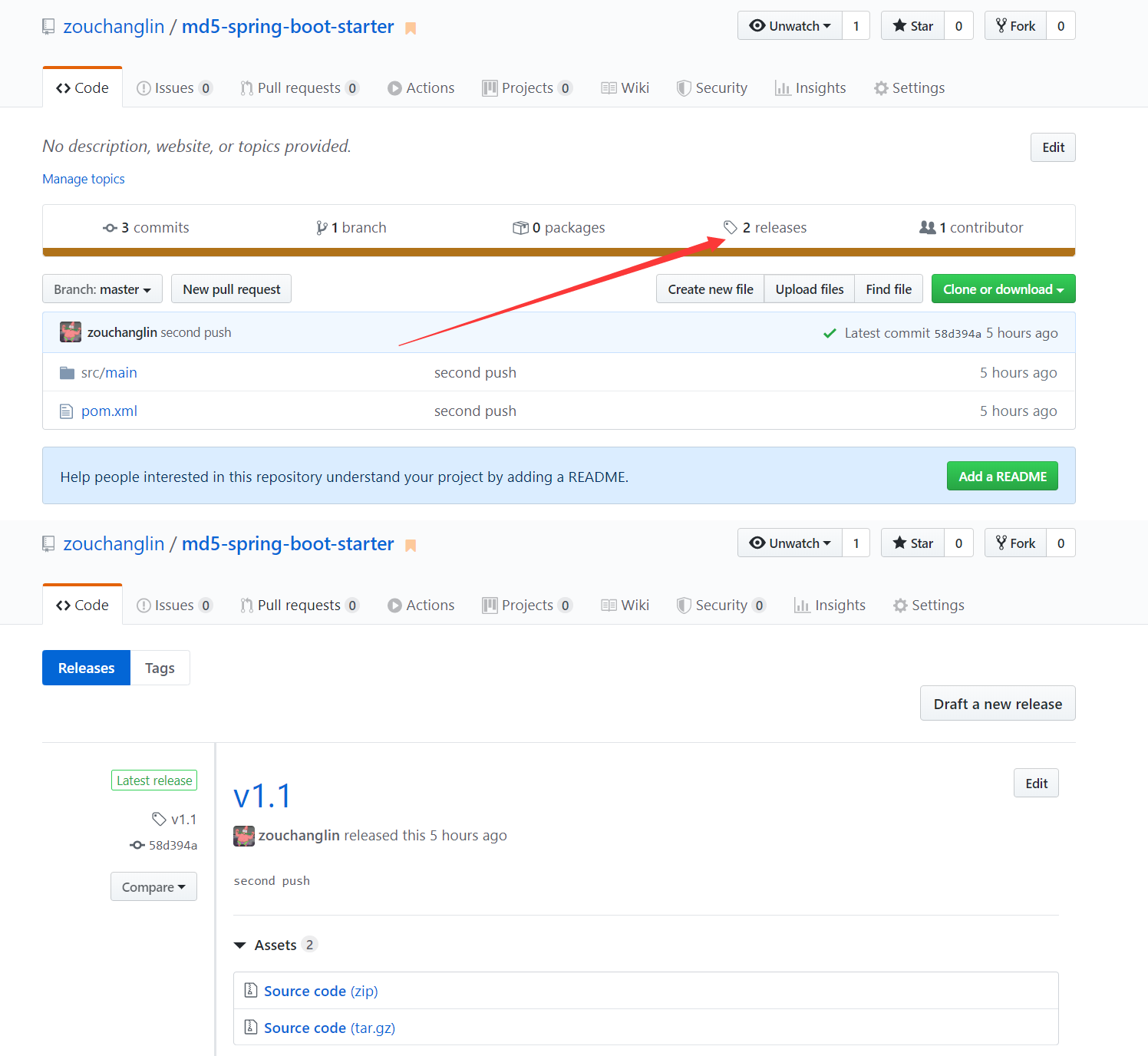
然后在jitpack授权,授权之后即可看到自己的仓库和Release版本:
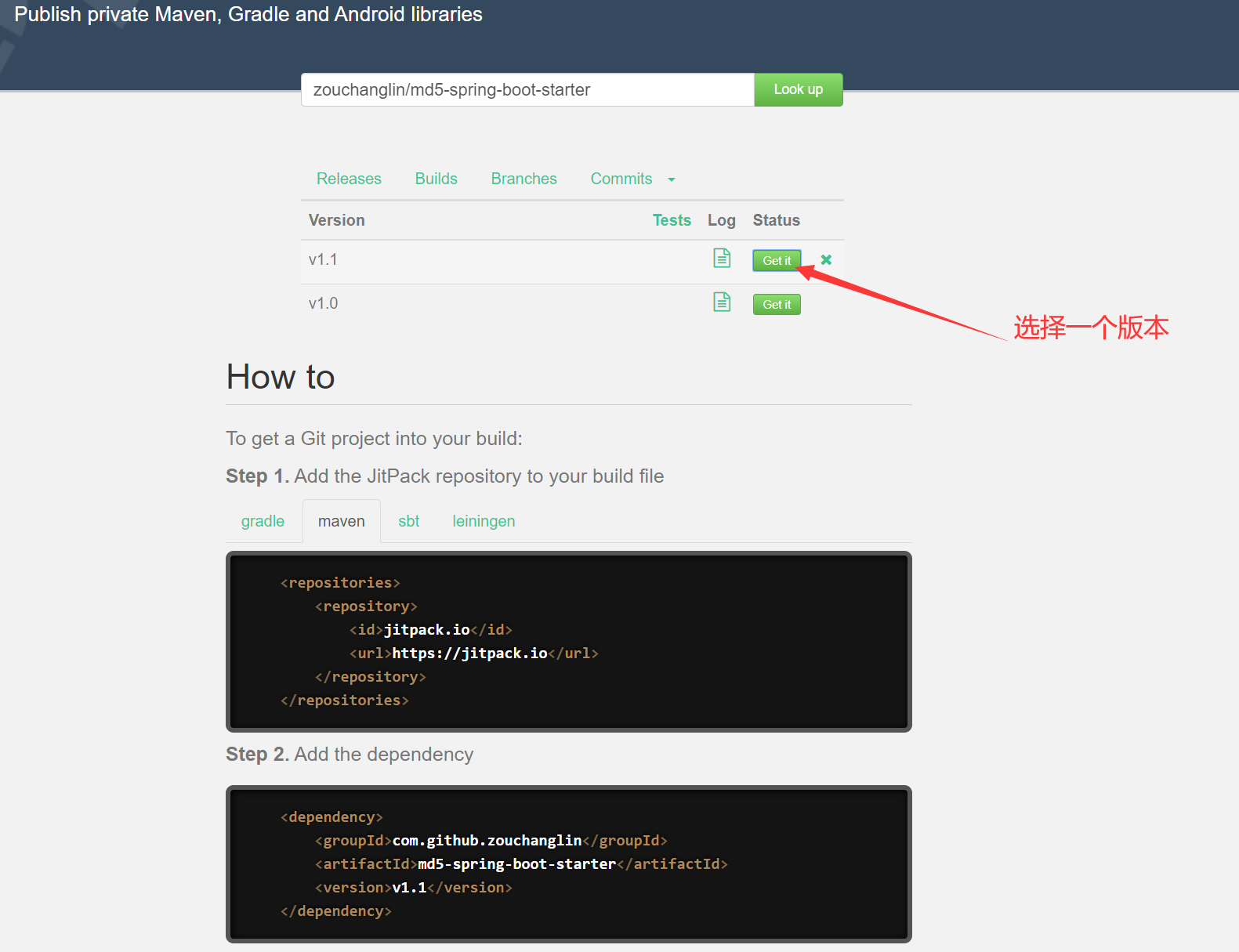
最后,在需要的项目中引入即可:
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>jitpack.io</id>
<url>https://jitpack.io</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.zouchanglin</groupId>
<artifactId>md5-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>v1.1</version>
</dependency>