自定义View(二)
前面的文章介绍了自定义View的需要准备的基础知识,自定义View的属性获取、测量(Measure)过程,Measure过程是为了计算View的大小。本篇文章主要记载一下自定义View过程中的Layout过程,Layout过程用于计算View的位置。另外还有更关键的一步,那就是绘制(Draw)过程,一切都准备好了就需要开始绘制出我们的自定义View,后面会有一个绘制例子,在该示例中绘制了一个圆形且带有进度文字说明的进度条,通过这个示例切实感受一下自定义View的魅力。最后还有一个重点就是自定义View状态的存储与恢复。
Layout过程
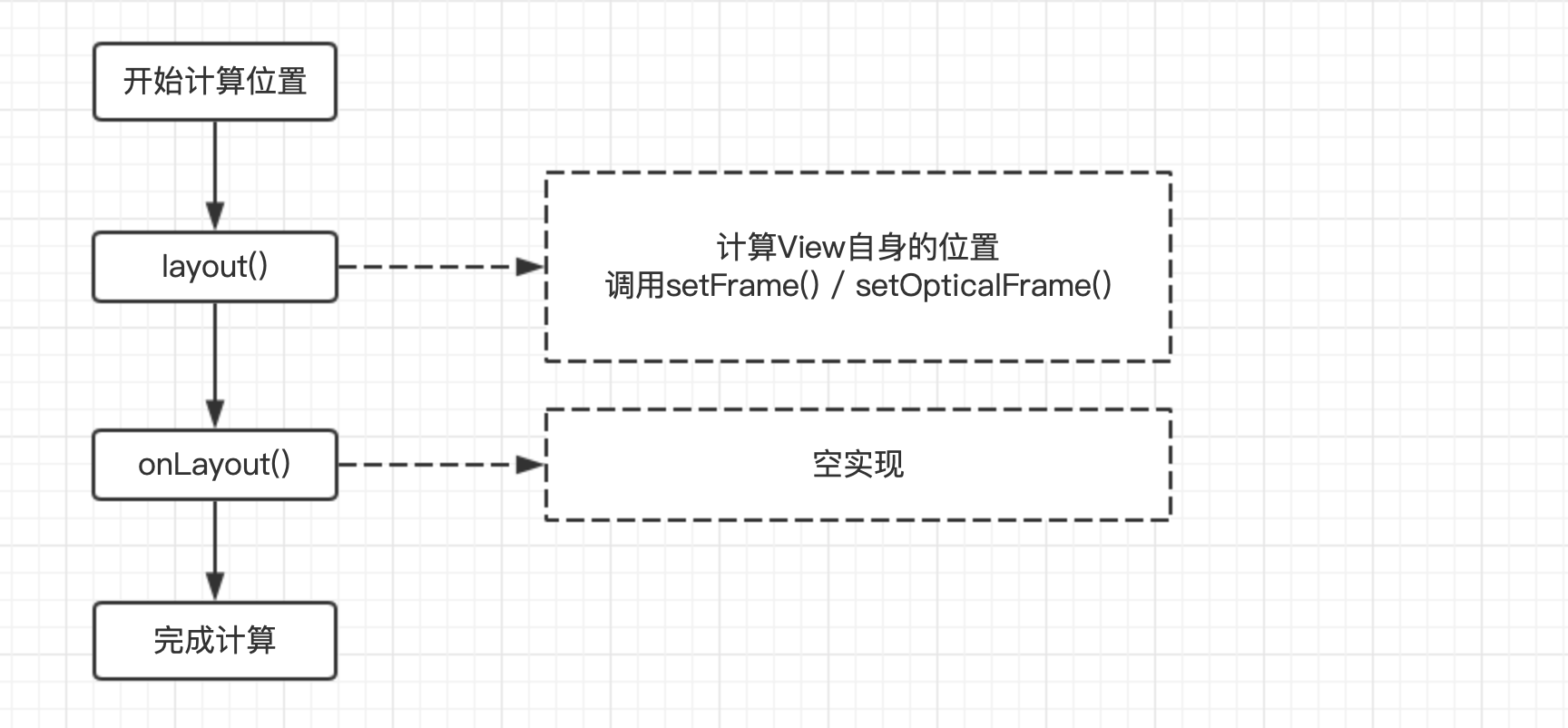
前面说了在自定义View的时候,我们需要测量出View的宽和高,在某些情况下,需要多次测量才能确定View最终的宽/高;该情况下,Measure过程后得到的宽和高可能不准确,因此最好是在Layout过程中通过onLayout()方法去获取最终的宽和高。Layout过程用于计算View的位置,即计算View的四个顶点位置:Left、Top、Right、Bottom,还记得View的位置定义吗?
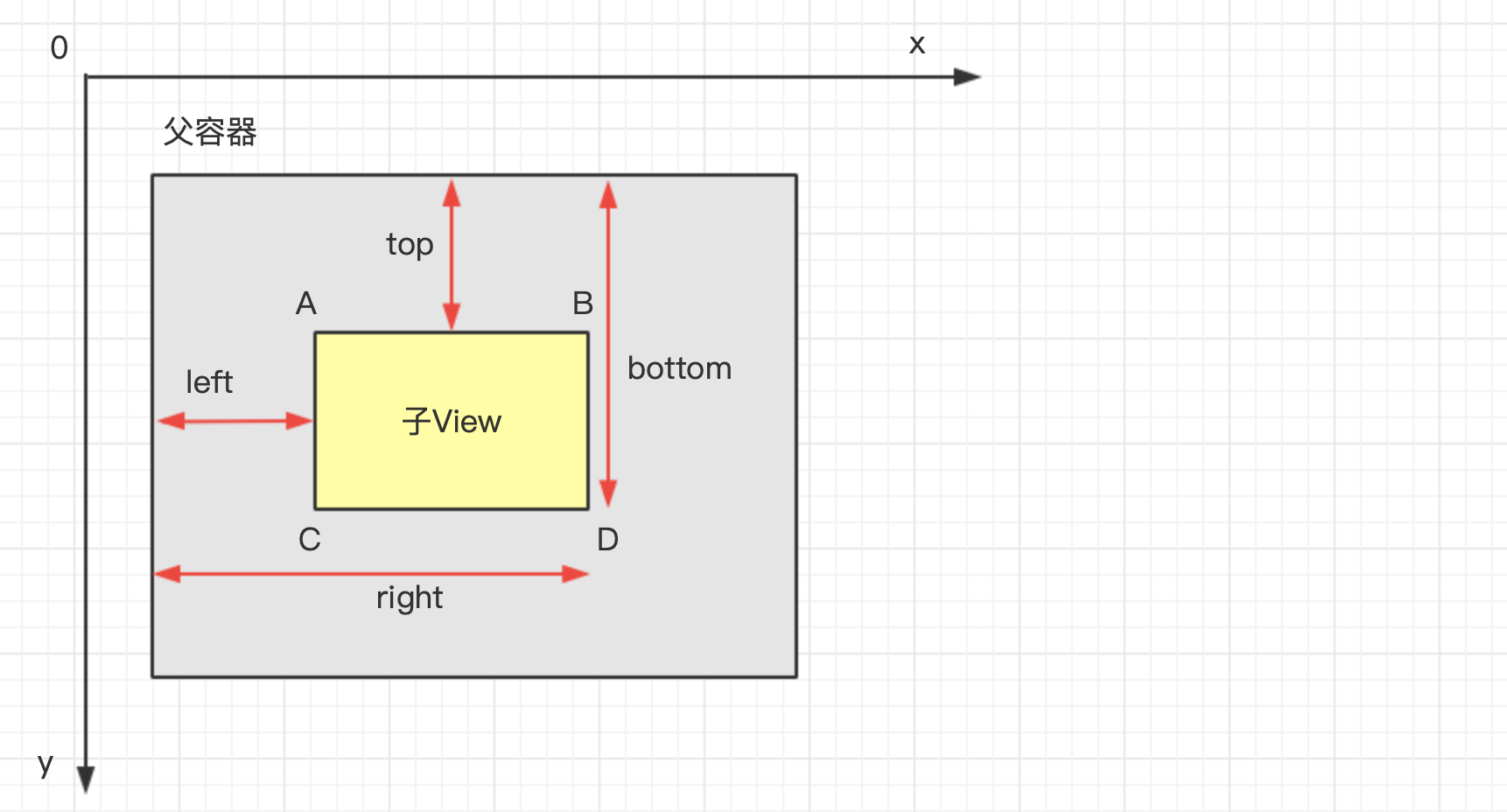 Layout过程也可以根据View的类型分为2种情况:对于单一View,仅仅需要计算本身View的位置即可。对于ViewGroup,除了计算自身View的位置外,还需要确定子View在父容器中的位置,即遍历调用所有子元素的measure()并且各子元素再递归去执行该流程。View树的位置是由包含的每个子视图的位置所决定的,所以如果想要计算整个View树的位置,则需递归计算每个子视图的位置,这与measure过程非常相似。
Layout过程也可以根据View的类型分为2种情况:对于单一View,仅仅需要计算本身View的位置即可。对于ViewGroup,除了计算自身View的位置外,还需要确定子View在父容器中的位置,即遍历调用所有子元素的measure()并且各子元素再递归去执行该流程。View树的位置是由包含的每个子视图的位置所决定的,所以如果想要计算整个View树的位置,则需递归计算每个子视图的位置,这与measure过程非常相似。
 getWidth()、getHeight()与 getMeasuredWidth()、getMeasuredHeight()获取的宽高有什么区别呢?其实getWidth()、getHeight()是获得View最终的宽和高,而getMeasuredWidth()、getMeasuredHeight()是获得View测量的宽和高。一般情况下二者获取的宽和高是相等的,但是通过重写View的layout()方法强行设置后就会导致二者得到的结果不一致,所以在非人为设置的情况下,View的最终宽高getWidth()、getHeight()与View的测量宽高getMeasuredWidth()、getMeasuredHeight()永远是相等的。
getWidth()、getHeight()与 getMeasuredWidth()、getMeasuredHeight()获取的宽高有什么区别呢?其实getWidth()、getHeight()是获得View最终的宽和高,而getMeasuredWidth()、getMeasuredHeight()是获得View测量的宽和高。一般情况下二者获取的宽和高是相等的,但是通过重写View的layout()方法强行设置后就会导致二者得到的结果不一致,所以在非人为设置的情况下,View的最终宽高getWidth()、getHeight()与View的测量宽高getMeasuredWidth()、getMeasuredHeight()永远是相等的。
Draw过程
Draw过程就是为了绘制出View视图,借助Paint、Canvas类,可以很轻松的实现绘制很多种图形,同时Draw也分为绘制单个View还是绘制ViewGroup,为了避免不必要的复杂度,示例中都是绘制单个View,所以Draw过程就是学习画笔(Paint)与画布(Canvas)的使用。
// 绘制
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
// 绘制圆
canvas.drawCircle(getWidth()/2, getHeight()/2, getHeight()/2 - paint.getStrokeWidth()/2, paint);
// 重新设置画笔宽度
paint.setStrokeWidth(2);
// 绘制直线
canvas.drawLine(0, getWidth()/2, getWidth(), getHeight()/2, paint);
canvas.drawLine(getWidth()/2, 0, getWidth()/2, getHeight(), paint);
// 绘制文本
paint.setTextSize(72);
paint.setStyle(Paint.Style.FILL);
paint.setStrokeWidth(0);
String stringTest = "Tim"
canvas.drawText(stringTest, 0, stringTest.length(), 0, getHeight(), paint);
}
invalidate()方法用于刷新View,本质是调用View的onDraw()重新绘制。在主线程之外,用postInvalidate()。requestLayout()方法和invalidate()方法恰恰相反,requestLayout()方法只调用measure()和layout()过程,不会调用draw(),不会重新绘制任何视图包括该调用者本身。
canvas.save()与canvas.restore()用于保存/恢复画布的状态,比如我现在为了绘图方便需要将画图旋转90°,但是我又希望只是在这一段绘制过程中才需要旋转画布,于是需要将之前正常的画布存储起来,然后旋转画布90°,用完了再恢复为正常状态:
canvas.save(); //这时候保存的是画布没旋转之前的状态
canvas.rotate(90, px / 2, py / 2); // 画布开始旋转
canvas.drawLine(......); // 收到旋转操作的影响
canvas.drawLine(......); // 收到旋转操作的影响
canvas.restore(); // 还原正常状态
对于translate()方法与rotate()方法,可以将它们理解为是画布平移,画布翻转,但是把它理解为坐标系的平移与翻转则会更加形象。前面的文章中说了,默认绘图坐标零点位于屏幕左上角,那么在调用translate(x, y)方法之后,则将原点(0,0)移动到了(x, y)。之后的所有绘图操作都将以(x, y)为原点执行。同理,rotate()方法也是一样,它将坐标系旋转了一定的角度。大家也许会想,这样的操作有什么用呢?的确,没有这两个方法,同样可以绘图,只要算好坐标,没有什么画不出来的。所以说,这些方法是Android用来帮助我们简化绘图而创建的。
状态的恢复与存储
很多时候我们为获得在视图中自由绘制的能力,需要创建一个继承于View类的定制类,然后重写onTouchEvent方法处理触摸事件,重写onDraw绘制自定义视觉效果,但这里可能会被一个问题困扰,那就是设备旋转导致数据丢失的问题,好在View类为我们提供了onSaveInstanceState和onRestoreInstanceState两个方法,虽然这两个方法和Activity两个方法很相似,但是千万别认为是一样的,因为他们的使用方法完全不同。 看看下面这个示例吧:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tim="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<!-- 必须加上Id,方便系统重建 -->
<cn.tim.custom_view.TestView
android:id="@+id/tv"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
tim:test_bool="true"
tim:test_dimension="100dp"
tim:test_enum="top"
tim:test_integer="10086"
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"/>
</RelativeLayout>
对于自己的自定义View要想保存状态必须加上ID android:id="@+id/xxx",这样系统才能正确找到需要保存状态的View。
// 为了演示重建后的数据恢复
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
// 点击此View的时候更新要显示的文字
stringTest = "Jone";
invalidate();
return true;
}
// UI重建后数据的保存
private static final String INSTANCE = "instance";
private static final String KEY_TEXT = "key_text";
@Nullable
@Override
protected Parcelable onSaveInstanceState() {
Bundle bundle = new Bundle();
bundle.putString(KEY_TEXT, stringTest);
bundle.putParcelable(INSTANCE, super.onSaveInstanceState());
return bundle;
}
@Override
protected void onRestoreInstanceState(Parcelable state) {
if(state instanceof Bundle){
Bundle bundle = (Bundle) state;
Parcelable parcelable = bundle.getParcelable(INSTANCE);
super.onRestoreInstanceState(parcelable);
stringTest = bundle.getString(KEY_TEXT);
return;
}
super.onRestoreInstanceState(state);
}
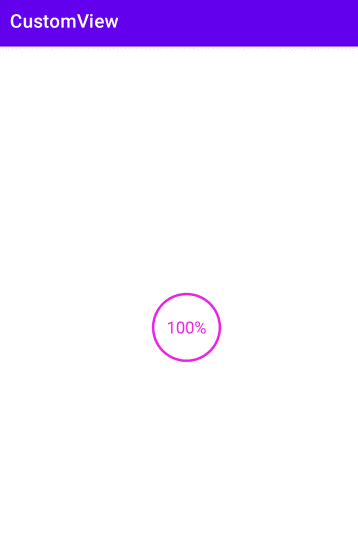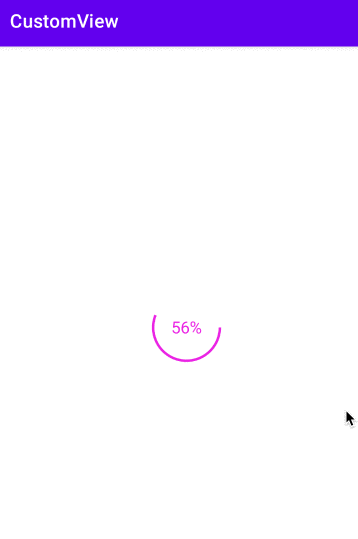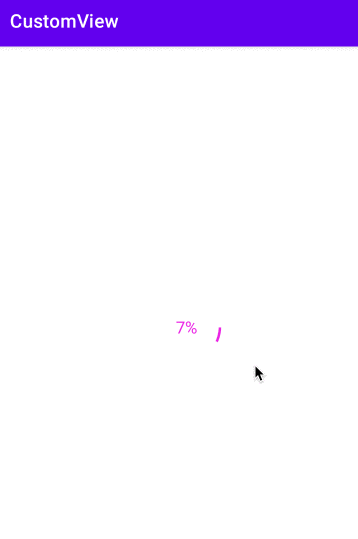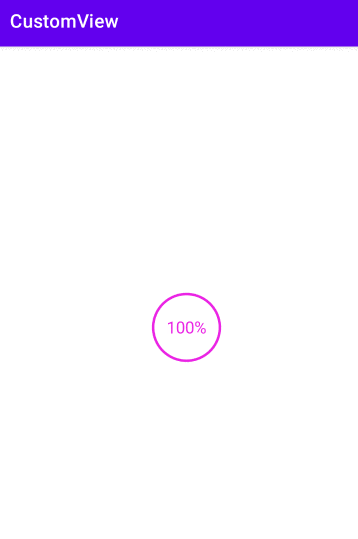
自定义一个圆形进度条
在attrs.xml声明自定义View需要的属性:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<resources>
<declare-styleable name="RoundProgressBar">
<attr name="color" format="color"/>
<attr name="line_width" format="dimension"/>
<attr name="radius" format="dimension"/>
<attr name="android:progress" />
<attr name="android:textSize" />
</declare-styleable>
</resources>
编写自定义View类:RoundProgressBar.java
package cn.tim.custom_view;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.res.TypedArray;
import android.graphics.Canvas;
import android.graphics.Paint;
import android.graphics.Rect;
import android.graphics.RectF;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.Parcelable;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.util.TypedValue;
import android.view.View;
public class RoundProgressBar extends View {
private int mRadius;
private int mColor;
private int mLineWidth;
private int mTextSize;
private int mProgress;
private Paint mPaint;
public RoundProgressBar(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
TypedArray ta = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.RoundProgressBar);
mRadius = (int) ta.getDimension(R.styleable.RoundProgressBar_radius, dp2px(30));
mColor = ta.getColor(R.styleable.RoundProgressBar_color, 0xffff0000);
mLineWidth = (int) ta.getDimension(R.styleable.RoundProgressBar_line_width, dp2px(3));
mTextSize = (int) ta.getDimension(R.styleable.RoundProgressBar_android_textSize, dp2px(36));
mProgress = ta.getInt(R.styleable.RoundProgressBar_android_progress, 30);
ta.recycle();
initPaint();
}
private float dp2px(int dpVal) {
return TypedValue.applyDimension(TypedValue.COMPLEX_UNIT_DIP, dpVal, getResources().getDisplayMetrics());
}
private void initPaint() {
mPaint = new Paint();
mPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
mPaint.setColor(mColor);
}
public void setProgress(int progress) {
mProgress = progress;
invalidate();
}
public int getProgress() {
return mProgress;
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int widthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int width = 0;
if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
width = widthSize;
} else {
int needWidth = measureWidth() + getPaddingLeft() + getPaddingRight();
if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
width = Math.min(needWidth, widthSize);
} else {
width = needWidth;
}
}
int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int heightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
int height = 0;
if (heightMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
height = heightSize;
}else {
int needHeight = measureHeight() + getPaddingTop() + getPaddingBottom();
if (heightMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
height = Math.min(needHeight, heightSize);
} else { //MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED
height = needHeight;
}
}
setMeasuredDimension(width, height);
}
private int measureHeight()
{
return mRadius * 2;
}
private int measureWidth()
{
return mRadius * 2;
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
mPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
mPaint.setStrokeWidth(mLineWidth * 1.0f / 4);
int width = getWidth();
int height = getHeight();
mPaint.setStrokeWidth(mLineWidth);
canvas.save();
canvas.translate(getPaddingLeft(), getPaddingTop());
float angle = mProgress * 1.0f / 100 * 360;
canvas.drawArc(new RectF(0, 0, width - getPaddingLeft() * 2, height - getPaddingLeft() * 2), 0, angle, false, mPaint);
canvas.restore();
String text = mProgress + "%";
mPaint.setStrokeWidth(0);
mPaint.setTextAlign(Paint.Align.CENTER);
mPaint.setTextSize(mTextSize);
int y = getHeight() / 2;
Rect bound = new Rect();
mPaint.getTextBounds(text, 0, text.length(), bound);
int textHeight = bound.height();
mPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.FILL);
canvas.drawText(text, 0, text.length(), getWidth() / 2, y + textHeight / 2, mPaint);
mPaint.setStrokeWidth(0);
}
private static final String INSTANCE = "instance";
private static final String KEY_PROGRESS = "key_progress";
@Override
protected Parcelable onSaveInstanceState() {
Bundle bundle = new Bundle();
bundle.putInt(KEY_PROGRESS, mProgress);
bundle.putParcelable(INSTANCE, super.onSaveInstanceState());
return bundle;
}
@Override
protected void onRestoreInstanceState(Parcelable state) {
if (state instanceof Bundle) {
Bundle bundle = (Bundle) state;
Parcelable parcelable = bundle.getParcelable(INSTANCE);
super.onRestoreInstanceState(parcelable);
mProgress = bundle.getInt(KEY_PROGRESS);
return;
}
super.onRestoreInstanceState(state);
}
}
在activity_main.xml中使用:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tim="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<cn.tim.custom_view.RoundProgressBar
android:id="@+id/id_pb"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:padding="10dp"
android:progress="0"
android:textSize="18sp"
tim:color="#ea22e4"
tim:radius="36dp"
/>
</RelativeLayout>
在MainActivity.java动态更新进度:
package cn.tim.custom_view;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.animation.ObjectAnimator;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
final View view = findViewById(R.id.id_pb);
view.setOnClickListener((v)-> ObjectAnimator.ofInt(view, "progress", 0, 100).setDuration(3000).start());
}
}