MyBatis(一)
MyBatis简介
首先说一下MyBatis是什么?MyBatis就是下图中的鸟,哈哈!
 MyBatis是一款优秀的持久层框架,它支持定制化SQL、存储过程以及高级映射。MyBatis避免了几乎所有的JDBC代码和手动设首参数以及获取结果集。MyBatis可以使用简单的XML或注解来配罝和映射原生信息,将接口和Java的POJOs(Plain Old Java Objects,普通的Java对象)映射成数据库中的记录
MyBatis是一款优秀的持久层框架,它支持定制化SQL、存储过程以及高级映射。MyBatis避免了几乎所有的JDBC代码和手动设首参数以及获取结果集。MyBatis可以使用简单的XML或注解来配罝和映射原生信息,将接口和Java的POJOs(Plain Old Java Objects,普通的Java对象)映射成数据库中的记录
MyBatis和Hibernate一样,是一个ROM框架(Object Relational Mapping,是对象到关系的映射,是一种解决实体对象与关系型数据库相互匹配的技术,它的实现思想就是将数据库中数据表映射成为对象,对关系型数据以对象的形式进行操作。在软件开发中,对象和关系数据是业务实体的两种表现形式,ORM通过使用描述对象和数据库之间映射的元数据,将对象自动持久化到关系数据库中。
MyBatis相对于Hibernate来说更加轻量级,所以MyBatis其实不具备像Hibernate那样自动建表的功能,但是MyBatis现在对我来说足够用了,现在开始记录一下学习MyBatis过程中遇到的问题或者MyBatis的知识点!
从HelloWorld开始
下面从MyBatis的helloworld说起,如何开始学习MyBatis: 首先是MyBatis的官方网站,这里具有最齐全的MyBatis文档,关键是居然有中文版的!?!?http://www.mybatis.org/mybatis-3/zh/index.html 另外,这个文档有PDF版本的,可以在网上下载到,如果你希望使用离线版的文档去下载这个PDF即可!
这个是MyBatis的maven依赖,如果没学过maven也不要紧,可以参考我的一片博客 《一文读懂Maven》 ,题目有点夸张,大家将就着看吧!如果你不希望使用maven的话直接导入jar包就好了,MyBatis只有一个jar包(但是不要忘记mysql驱动程序的jar包)!
1<dependency>
2 <groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
3 <artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
4 <version>x.x.x</version>
5</dependency>
我就演示一下非maven版本的HelloWorld,首先准备一个数据库和表,如图:
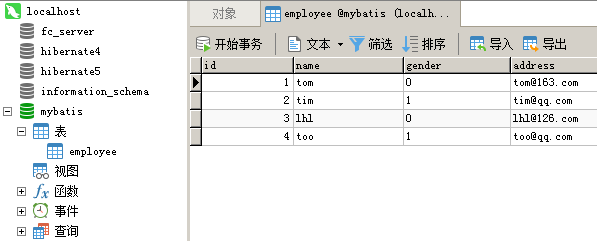 这是我整个工程的目录结构:
这是我整个工程的目录结构:
 resource.xml
resource.xml
1<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
2
3<!DOCTYPE configuration
4PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
5"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
6<configuration>
7 <environments default="development">
8 <environment id="development">
9 <transactionManager type="JDBC" />
10 <dataSource type="POOLED">
11 <property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" />
12 <property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/mybatis" />
13 <property name="username" value="root" />
14 <property name="password" value="1234" />
15 </dataSource>
16 </environment>
17 </environments>
18 <mappers>
19 <mapper resource="com/xpu/bean/Employee.xml" />
20 </mappers>
21
22</configuration>
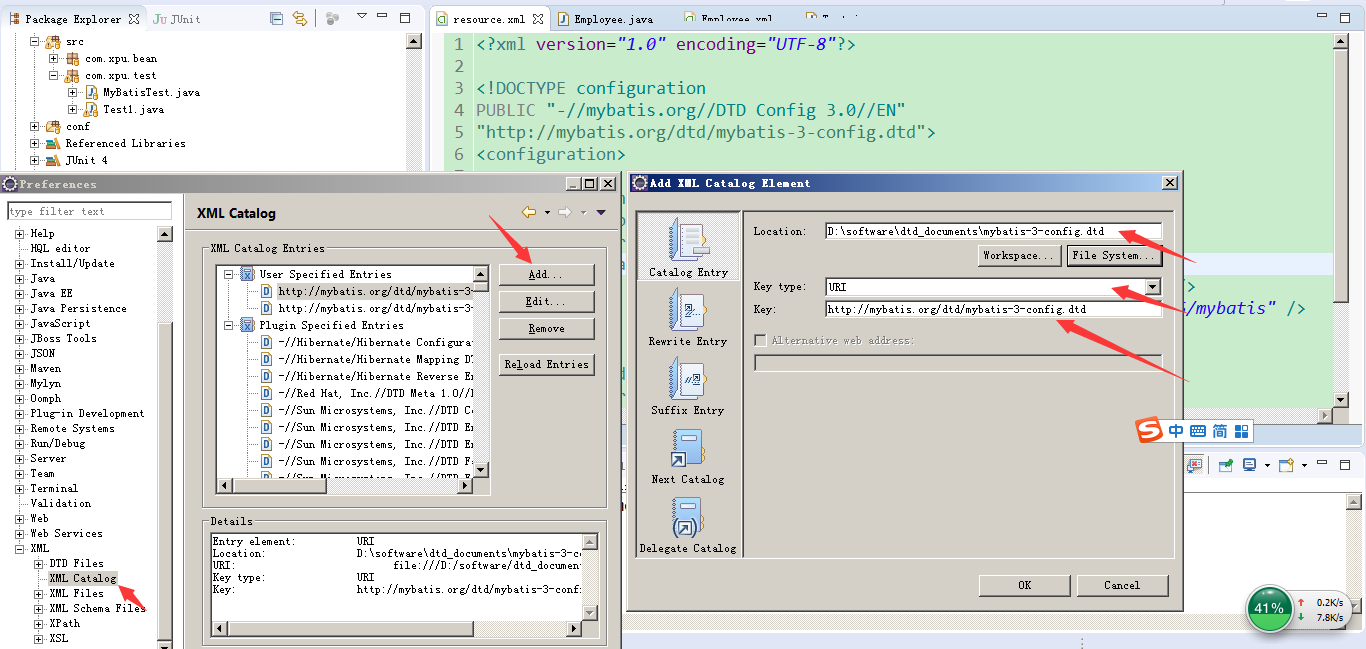
dataSource 标签配置的数据库连接的基本信息,mappers标签配置的是对象映射关系文件,说一下关于引入dtd约束文档的问题,如果未配置dtd约束文档,那么eclipse是没有提示的,你可以在Window—>Preference–>XML—>XMLCatalog里面配置dtd,点击Add,选择URL,填入dtd的URL,选择FileSystem点击打开下载好的dtd文件即可!
 接着创建一个JavaBean:
接着创建一个JavaBean:
1package com.xpu.bean;
2
3public class Employee {
4 private Integer id;
5 private String name;
6 private char gender;
7 private String address;
8 public Employee() {
9 super();
10 }
11 public Employee(Integer id, String name, char gender, String address) {
12 super();
13 this.id = id;
14 this.name = name;
15 this.gender = gender;
16 this.address = address;
17 }
18 public Integer getId() {...}
19 public void setId(Integer id) {...}
20 public String getName() {...}
21 public void setName(String name) {...}
22 public char getGender() {...}
23 public void setGender(char gender) {...}
24 public String getAddress() {...}
25 public void setAddress(String address) {...}
26 @Override
27 public String toString() {...}
28}
创建关系映射文件employee.xml,注意namespace必须和JavaBean一一对应,sql查询语句不要写错,id是要传入的一个参数:
1<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
2<!DOCTYPE mapper
3PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
4"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
5<mapper namespace="com.xpu.bean.Employee">
6 <select id="selOne" parameterType="java.lang.String" resultType="com.xpu.bean.Employee">
7 select * from employee where id = #{id}
8 </select>
9</mapper>
Test.java
1package com.xpu.bean;
2
3import java.io.IOException;
4import java.io.Reader;
5
6import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;
7import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
8import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
9import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;
10
11public class Test {
12 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
13 //通过resource.xml中的配置信息获取一个SqlSessionFactory对象
14 Reader reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader("resource.xml");
15 SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFty = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader);
16
17 //开始一个会话
18 SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFty.openSession();
19
20 //执行查询方法
21 Employee one = sqlSession.selectOne("com.xpu.bean.Employee.selOne", "1");
22 System.out.println(one);
23
24 //关闭会话
25 sqlSession.close();
26 }
27}
 这便查询到了ID为1的用户,HelloWorld的演示到此结束!
这便查询到了ID为1的用户,HelloWorld的演示到此结束!
MyBatis的开发模式
1、配置文件
resource.xml
Employee.xml
1<mapper namespace="com.xpu.bean.Employee">
2 <select id="selOne" parameterType="java.lang.String" resultType="com.xpu.bean.Employee">
3 select * from employee where id = #{id}
4 </select>
5</mapper>
这样的方式就是我的HelloWorld中所用到的方式,Employee.xml的namespace是我的JavaBean,执行查询的时候需要使用如下方式,selOne是select标签的id,parameterType代表参数的类型,resultType代表返回值的类型,中间是sql查询语句!
2、接口
IEmployeeDao.java
1public interface IEmployeeDao {
2 //查询所有记录
3 @Select("select * from employee")
4 public List<Employee> getAll();
5}
resource.xml
使用该模式测试:
1package com.xpu.dao;
2
3import java.io.IOException;
4import java.io.Reader;
5import java.util.List;
6
7import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;
8import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
9import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
10import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;
11
12import com.xpu.bean.Employee;
13
14public class Test {
15 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
16 Reader reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader("resource.xml");
17 SqlSessionFactory factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader);
18
19 //true表示是否自动提交,默认值是false
20 SqlSession session = factory.openSession(true);
21
22 IEmployeeDao mapper = session.getMapper(IEmployeeDao.class);
23 List<Employee> all = mapper.getAll();
24 for (Employee employee : all) {
25 System.out.println(employee);
26 }
27 }
28}
3、接口+配置文件
这种模式是最常用的模式: Employee.xml:
1<mapper namespace="com.xpu.dao.IEmployeeDao">
2 <select id="getAll" resultType="com.xpu.bean.Employee">
3 select * from employee
4 </select>
5
6 <select id="getOne" resultType="com.xpu.bean.Employee">
7 select * from employee where id = #{id}
8 </select>
9</mapper>
resource.xml
IEmployeeDao.java
1package com.xpu.dao;
2public interface IEmployeeDao {
3
4 public List<Employee> getAll();
5
6 public Employee getOne(String id);
7}
以上就是MyBatis的三种开发模式,第三种用的比较多,第一种局限性较大,第二种耦合度太强,开发本来的原则就是高内聚、低耦合,使用第二种方式反倒是的耦合度增强不宜使用,所以常用的方式就是第三种开发模式!
下面对需要注意的地方总结一下,参数类型的配置要写全路径名称,避免出错,使用第二种开发模式的时候,需要将接口配置成class,定义返回值类型的时候注意,虽然getAll返回的是一个List集合,但是集合中装的还是对象,所以我们在配置返回值的时候还是需要配置成Employee类:
1<mapper class="com.xpu.dao.IEmployeeDao"/>
最后说一个比较重要的问题,为什么我们通过IEmployeeDao.class对象得到的mapper对象是一个实例呢?我们并没有实现接口呀?没有实现接口的话为什么可以拿到他的实现类对象呢?
这是其实是个代理对象,是通过动态代理来实现的,具体参考Proxy类,看看如何通过动态代理生成代理对象,具体可以参考 《Mybatis是如何通过mapper接口生成代理对象的》
MyBatis的CURD
MyBatis最核心的作用还是增删改查嘛,接下来我通过第三种开发模式总结一下MyBatis的CURD,看看Employee.xml中的SQL语句:
1<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
2<!DOCTYPE mapper
3PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
4"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
5<mapper namespace="com.xpu.dao.EmployeeDao">
6
7 <select id="selAll" resultType="com.xpu.bean.Employee">
8 select * from employee
9 </select>
10
11 <select id="selOne" parameterType="java.lang.String" resultType="com.xpu.bean.Employee">
12 select * from employee where id = #{id}
13 </select>
14
15 <insert id="insertEmp" parameterType="com.xpu.bean.Employee">
16 insert into employee values(#{id}, #{name}, #{gender}, #{address})
17 </insert>
18
19 <update id="updateEmp" parameterType="com.xpu.bean.Employee">
20 update employee set name = #{name}, address = #{address} where id = #{id}
21 </update>
22
23 <delete id="daleteEmp">
24 delete from employee where id = #{id}
25 </delete>
26</mapper>
IEmployeeDao.java
1public interface EmployeeDao {
2 //查询所有
3 public List<Employee> selAll();
4
5 //查询单一
6 public Employee selOne(String id);
7
8 //新增
9 public void insertEmp(Employee emp);
10
11 //修改
12 public void updateEmp(Employee emp);
13
14 //删除
15 public void daleteEmp(String id);
16}
测试代码:
1public class Demo {
2 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
3 Reader reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader("resource.xml");
4 SqlSessionFactory sessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader);
5 SqlSession session = sessionFactory.openSession();
6
7 IEmployeeDao mapper = session.getMapper(IEmployeeDao.class);
8 mapper.insertEmp(new Employee(5, "Lucy", '1', "Lucy@163.com"));
9 mapper.daleteEmp("4");
10 mapper.updateEmp(new Employee(5, "Lucy", '1', "Lucy@qq.com"));
11 System.out.println(mapper.selOne("2"));
12 session.commit();
13 session.close();
14 }
15}
MyBatis的传参
1、出错演示
好了,增删查改的基本功能已经演示完毕,但是假设我们需要做一个多条件查询的方法,则需要这样写(一下代码均为省略代码,只贴上了重要的代码,其他的代码均在CURD的演示中): Employee.xml
1<select id="queryList" resultType="com.xpu.bean.Employee">
2 select * from employee where name like '#{name}%' and gender = #{gender}
3</select>
IEmployeeDao.java
多条件查询测试:
1public void test() {
2 IEmployeeDao mapper = session.getMapper(IEmployeeDao.class);
3 List<Employee> list = mapper.queryList("t", '1');
4 for (Employee employee : list) {
5 System.out.println(employee);
6 }
7}
但是却报错了,注意红线标记的地方,我们需要修改参数的传递方式:

2、顺序传参法
其实对于这种多参数的情况,应该这样写Employee.xml,这叫做顺序传参法:
1<select id="queryList" resultType="com.xpu.bean.Employee">
2 select * from employee where name like '${param1}%' and gender = #{param2}
3 select * from employee where name = #{0} and gender = #{1}
4</select>
#{ }里面的数字代表你传入参数的顺序,SQL语句的语义表达不直观,且一旦顺序调整容易出错,所以不建议使用!
3、注解传参法
但是这样写的可读性太差,可以使用注解的方式:
1<select id="queryList" resultType="com.xpu.bean.Employee">
2 select * from employee where name like '${name}%' and gender = #{gender}
3</select>
1//多条件查询
2public List<Employee> queryList(@Param("name") String name, @Param("gender") char gender);
这样可读性强,而且不会因为参数的顺序问题导致程序异常!
4、Map传参法
Employee.xml
1<select id="queryList" resultType="com.xpu.bean.Employee">
2 select * from employee where name like '${name}%' and gender = #{gender}
3<select>
IEmployeeDao.java
1public List<Employee> queryList(Map map);
测试代码:
1public void test() {
2 IEmployeeDao mapper = session.getMapper(IEmployeeDao.class);
3 Map map = new HashMap();
4 map.put("name", "t");
5 map.put("gender", '1');
6 List<Employee> list = mapper.queryList(map);
7}
5、JavaBean传参法
这个在MyBatis的CURD中已经演示过了,resultType="com.xpu.bean.Employee" ,通过#{ 对象属性 } 便可以传参,在此不再赘述!
MyBatis动态SQL
MyBatis 的强大特性之一便是它的动态 SQL。你可以在这个网站学习动态SQL 《动态 SQL》 ,如果你有使用 JDBC 或其他类似框架的经验,你就能体会到根据不同条件拼接 SQL 语句有多么痛苦。拼接的时候要确保不能忘了必要的空格,还要注意省掉列名列表最后的逗号。利用动态 SQL 这一特性可以彻底摆脱这种痛苦。
if
就是简单的条件判断,利用if语句我们可以实现某些简单的条件选择
1<!-- 动态SQL -->
2 <select id="queryByIf" resultType="com.xpu.bean.Employee">
3 select * from employee where 1=1
4 <if test="name != null">
5 and name like '${name}%'
6 </if>
7 </select>
但是在上面的例子中,如果name为空的话,where后面就什么都没有,所以加上1=1完全是为了保证语法的正确性,这个问题将在下面解决!
where+if
where标签知道如果它包含的标签中有返回值的话,它就插入一个where。此外,如果标签返回的内容是以AND 或 OR开头的,则它会剔除掉。
1<select id="queryByWhere" resultType="com.xpu.bean.Employee">
2 select * from employee
3 <where>
4 <if test="name != null">
5 name like '${name}%'
6 </if>
7 <if test="address != null">
8 and address = #{address}
9 </if>
10 </where>
11</select>
上述例子中,如果name不为空,address不为空,则SQL语句是select * from employee where name like '${name}%' and address = #{address} ,即使name为空,address前面的and也会被去掉,同样是合法的SQL语句,如果都为空,那就变成了查询所有记录,同样也是合法的SQL语句!
trim
trim标签是可以让我们自己去实现一个where标签,或者实现更多的功能,下面用trim标签去实现一个where标签:
1<select id="queryByTrim" resultType="com.xpu.bean.Employee">
2 select * from employee
3 <trim prefix="where" prefixOverrides="AND | OR">
4 <if test="name != null">
5 name like '${name}%'
6 </if>
7 <if test="address != null">
8 and address = #{address}
9 </if>
10 </trim>
11 </select>
这个trim标签其实就是一个可以通过自定义属性去完成一些功能的标签,prefix="where" 就是代表如果标签中有内容则加上where,如果where后面直接遇到AND或者OR这样的标签就会将其剔除!
set
1<update id="updateEmployee" parameterType="com.xpu.bean.Employee">
2 update user
3 <set>
4 <if test="name!=null">
5 name=#{name}
6 </if>
7 </set>
8 <where>
9 <if test="address!=null">
10 address=#{address}
11 </if>
12 </where>
13</update>
set标签代替了sql中set关键字,set标签可以自动去除sql中的多余的',',这个和where标签是一样的道理,同样的我们可以使用trim来实现同样的功能:
1 <update id="updateEmployee" parameterType="com.xpu.bean.Employee">
2 update user
3 <trim prefix="set" prefixOverrides=",">
4 <if test="name!=null">
5 name=#{name}
6 </if>
7 </trim>
8 <where>
9 <if test="address!=null">
10 address=#{address}
11 </if>
12 </where>
13 </update>
choose
chose标签类似于流程控制中switch case default语句,配合when、otherwise标签使用:
1<select id="queryByChoose" resultType="com.xpu.bean.Employee">
2 select * from employee where 1=1
3 <choose>
4 <when test="name != null">
5 and name like '${name}%'
6 </when>
7 <when test="address != null">
8 and address = ${address}
9 </when>
10 <otherwise>
11 order by name
12 </otherwise>
13 </choose>
14 </select>
foreach
foreach标签可迭代任何对象(如列表、集合等)和任何的字典或者数组对象传递给foreach作为集合参数,下面是一个根据ID批量删除的示例:
1<delete id="deleteByList">
2 delete from employee where id in
3 <foreach collection="list" open="(" separator="," close=")"
4 item="myitem">
5 #{myitem}
6 </foreach>
7</delete>
8
9<delete id="deleteByArray">
10 delete from employee where id in
11 <foreach collection="array" open="(" separator="," close=")"
12 item="myitem">
13 #{myitem}
14 </foreach>
15</delete>
1//批量删除
2public Integer deleteByList(List<String> list);
3
4//批量删除
5public Integer deleteByArray(String[] strs);
1public void func() throws IOException {
2 Integer array = mapper.deleteByArray(new String[] {"1", "2"});
3 System.out.println("影响行数:" + array);
4
5 List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
6 list.add("3");
7 list.add("4");
8
9 Integer deleteByList = mapper.deleteByList(list);
10 System.out.println("影响行数:" + deleteByList);
11 session.commit();
12 session.close();
13 }
动态 SQL 语句的编写往往就是一个拼接的问题,为了保证拼接准确,我们最好首先要写原生的 SQL 语句出来,然后在通过 MyBatis 动态SQL 对照着改,防止出错!